Feed Your Garden Right: Understanding Organic Fertilizers
Share

When you walk past thriving gardens bursting with vibrant vegetables and lush flowers, you might wonder what secret these gardeners know. The answer often lies beneath the surface in something surprisingly simple: organic fertilizers. But with countless options flooding the market and conflicting advice online, understanding which organic fertilizer truly works for your garden can feel overwhelming.
This comprehensive guide breaks down everything you need to know about organic fertilizers, from their scientific benefits to practical application methods, helping you make informed decisions that will transform your garden naturally.
What Makes Organic Fertilizers Different?
Organic fertilizers derive from natural sources like plant matter, animal waste, and mineral deposits. Unlike synthetic fertilizers that provide quick nutrient bursts through chemically processed compounds, organic options feed both your plants and the living ecosystem in your soil.
The key difference lies in how these nutrients become available to plants. Synthetic fertilizers deliver nutrients in immediately soluble forms, which plants absorb rapidly but which can also leach away quickly or burn delicate roots. Organic fertilizers release nutrients gradually as soil microorganisms break down organic matter, creating a steady supply that matches plant needs while building long-term soil health.
The Science Behind Organic Plant Nutrition
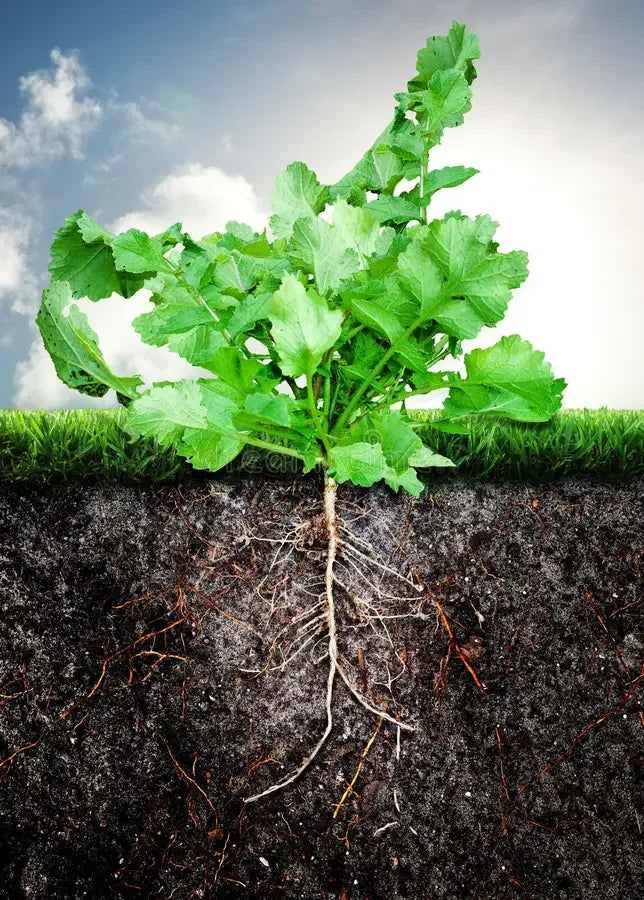

Understanding how organic fertilizers work requires looking at the soil as a living ecosystem. Healthy soil contains billions of microorganisms per handful, including bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and beneficial nematodes. These microscopic workers convert organic materials into plant-available nutrients while improving soil structure.
The Soil Food Web in Action: When you apply organic fertilizer, you're feeding both plants and beneficial microbes. These microorganisms secrete enzymes that break down complex organic compounds into simpler forms plants can absorb through their roots. This biological process, called mineralization, means nutrients release slowly and steadily rather than flooding the root zone all at once.
Modern organic fertilizers leverage this understanding by combining fast-acting liquid nutrients with beneficial microbes. For example, worm casting-based liquid fertilizers can contain hundreds of beneficial bacterial species that colonize root zones, suppress disease-causing pathogens, and produce plant growth hormones naturally.
Types of Organic Fertilizers Explained
Liquid Organic Fertilizers
Liquid fertilizers offer several advantages for today's gardeners. They provide faster nutrient availability than solid organics while maintaining biological benefits. Quality liquid organic fertilizers derived from worm castings deliver both immediately available nutrients and beneficial microbes in every application.
Key Benefits:
- Even distribution across all plant surfaces and soil
- Quick absorption through leaves and roots
- Easy application with watering cans or hose-end sprayers
- Consistent results without guesswork
- Suitable for indoor houseplants and outdoor gardens alike
Premium liquid options contain 250+ species of beneficial bacteria and fungi that establish healthy soil ecosystems, improving nutrient cycling and plant disease resistance over time.
Try Plant Juice: Our Premium Liquid Organic Fertilizer
Plant Juice features 291+ beneficial microbes in a worm casting-based formula that delivers fast results while building soil health. Perfect for all plants, indoor and outdoor. Covers 2,000 square feet at just 1.5 cents per square foot.
★★★★★ 4.8/5 from 1,960+ verified reviews
Shop Plant JuiceSolid Organic Amendments

Worm Castings (Vermicompost): Often called nature's perfect plant food, worm castings contain balanced nutrients, beneficial microbes, and humic acids that improve soil structure. They're gentler than synthetic fertilizers and won't burn plants even at high application rates. Learn more about premium worm castings.
Mushroom Compost: This rich organic material provides slow-release nutrition and improves soil moisture retention. It's particularly valuable for vegetable gardens and flower beds where steady nutrient availability throughout the growing season matters most.
Compost: Well-aged compost supplies moderate nutrients while dramatically improving soil structure, water retention, and microbial diversity. It's the foundation of organic gardening but works best when combined with more concentrated nutrient sources.
Understanding NPK: What Your Plants Actually Need
Every fertilizer displays an NPK ratio showing nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) percentages. Understanding these primary macronutrients helps you choose appropriate fertilizers for specific plant needs.
Nitrogen (N): Drives leafy green growth and overall plant vigor. Essential for vegetables like lettuce, kale, and herbs. Deficiency symptoms include yellowing leaves and stunted growth.
Phosphorus (P): Supports root development, flowering, and fruit production. Critical during transplanting and for fruiting crops like tomatoes and peppers.
Potassium (K): Strengthens plant immunity, improves drought tolerance, and enhances fruit quality. Helps plants resist diseases and environmental stress.
Organic Fertilizers vs. Synthetic: Making the Right Choice
While synthetic fertilizers promise quick results, they come with hidden costs that affect long-term garden health and environmental sustainability.
Synthetic Fertilizer Drawbacks:
- Kills beneficial soil microorganisms through salt accumulation
- Requires increasing applications as soil life depletes
- Leaches into groundwater, causing environmental pollution
- Can burn plant roots with overapplication
- Provides no organic matter to improve soil structure
Organic Fertilizer Advantages: Builds soil health with each application, feeds beneficial microbes that protect plant roots, releases nutrients gradually to reduce waste, improves soil structure and water retention, and remains safe for children, pets, and wildlife.
The best organic fertilizers deliver results comparable to synthetics while actually improving your soil over time. Modern worm casting-based liquid fertilizers bridge the gap between fast-acting results and long-term soil building.
How to Apply Organic Fertilizers for Maximum Results

Liquid Fertilizer Application
For Vegetable Gardens: Apply every 2-3 weeks during active growth. Mix according to label directions and water thoroughly into the root zone. For 2,000 square feet of garden space, a 32-ounce bottle of quality liquid organic fertilizer typically provides one complete treatment at approximately 1.5 cents per square foot.
For Houseplants: Feed every 2-4 weeks during spring and summer, reducing to monthly during fall and winter. Apply until water drains from pot bottom, ensuring even distribution throughout the root zone. Check out our complete houseplant care guide for more tips.
For Lawns: Apply in early spring, late spring, summer, and fall for lush, green growth without harsh chemicals that can harm family members or pets. Read more in our organic lawn care guide.
Solid Amendment Application
Spring Garden Prep: Work 2-4 inches of compost or aged mushroom compost into planting beds before spring planting. Add worm castings directly to transplant holes at 1/4 to 1/2 cup per plant.
Mid-Season Feeding: Side-dress growing plants with worm castings or compost, working gently into the top inch of soil around plant bases without disturbing roots.
Fall Soil Building: Apply generous layers of organic amendments after harvest, allowing them to break down over winter and enrich soil for spring planting.
Complete Your Organic Garden System
Combine Plant Juice liquid fertilizer with Ancient Soil premium worm castings for the ultimate organic feeding program. Shop our money-saving bundles.
View BundlesCommon Organic Fertilizer Mistakes to Avoid
Even experienced gardeners sometimes make these preventable errors:
Overapplying Nitrogen-Rich Amendments: Too much nitrogen produces excessive leafy growth at the expense of flowers and fruit. Tomatoes and peppers particularly suffer from this imbalance, producing beautiful foliage but few actual vegetables.
Applying Fresh Manure: Uncomposted manure burns plants and may contain pathogens. Always use fully aged or composted manure products.
Ignoring Soil pH: Organic fertilizers work best in appropriate pH ranges. Test soil pH and adjust if necessary before expecting optimal results. Learn more about soil testing techniques.
Inconsistent Application: Organic fertilizers require regular application for best results. Unlike synthetic fertilizers that shock plants with concentrated nutrients, organic options work best with steady, consistent feeding schedules.
Not Watering Properly: Organic fertilizers need adequate moisture to activate microbial breakdown and nutrient release. Water thoroughly after applying solid amendments.
Building a Complete Organic Fertilization Program

Successful organic gardening combines multiple approaches for comprehensive plant nutrition:
Foundation Layer: Start with quality compost worked into beds annually, building organic matter and soil life.
Regular Feeding: Apply liquid organic fertilizers every 2-3 weeks during active growth for consistent nutrient availability.
Targeted Amendments: Add specific nutrients as needed based on plant requirements and soil test results.
Microbial Support: Ensure continuous beneficial microbe populations through regular applications of living fertilizers containing hundreds of bacterial species.
Special Considerations for Different Garden Types
Vegetable Gardens
Vegetables are heavy feeders requiring consistent nutrition throughout the growing season. Combine compost for soil building with regular liquid fertilizer applications for optimal harvest quality and quantity. Tomatoes, peppers, squash, and cucumbers particularly benefit from steady organic feeding that supports both vegetative growth and fruit production. Read our complete vegetable garden success guide.
Flower Gardens

Flowering plants need balanced nutrition with adequate phosphorus for bloom production. Apply liquid organic fertilizer every 2-3 weeks during blooming season. For spectacular flowers, try Bloom Juice, our award-winning formula specifically designed for bigger, longer-lasting blooms. Perennials benefit from spring and fall applications of compost or mushroom compost to maintain soil health year after year.
Container Gardens
Container plants exhaust soil nutrients quickly and need more frequent feeding than in-ground gardens. Apply diluted liquid organic fertilizer every 1-2 weeks during active growth. The confined root space means containers respond particularly well to microbially-rich liquid fertilizers that maximize nutrient availability in limited soil volume. Learn more about container gardening techniques.
Houseplants
Indoor plants thrive with regular light feeding rather than heavy periodic applications. Use liquid organic fertilizer at half strength every 2 weeks during spring and summer growth periods. The beneficial microbes in quality organic fertilizers help prevent root rot and other common houseplant problems while supporting healthy growth. Get expert tips in our comprehensive plant care guide.
Lawns
Organic lawn care builds thick, resilient turf that resists weeds, drought, and disease naturally. Apply liquid organic fertilizer in early spring, late spring, summer, and fall for deep green color without chemical exposure risks to children and pets.
The Environmental Impact of Your Fertilizer Choice
Your fertilizer decisions affect more than just your garden. Synthetic fertilizer runoff contributes to algal blooms that create dead zones in rivers, lakes, and coastal waters. These environmental disasters kill fish, destroy aquatic ecosystems, and contaminate drinking water sources.
Organic fertilizers release nutrients slowly, dramatically reducing runoff risks. The organic matter and microbial activity they support also improve soil water retention, meaning less irrigation and reduced water waste. By choosing organic fertilizers, you're voting for cleaner waterways and healthier ecosystems with every application.
Cost Comparison: Organic vs. Synthetic
Many gardeners assume organic fertilizers cost more, but proper comparison reveals surprising value. While organic options may have higher upfront costs per bottle or bag, they provide multiple benefits beyond basic nutrition:
- Improving soil structure reduces watering needs
- Building beneficial microbe populations suppresses diseases naturally
- Steady nutrient release means less frequent applications
- No risk of costly plant damage from over-application or burning
Quality liquid organic fertilizers covering 2,000 square feet at 1.5 cents per square foot compete favorably with synthetic options while delivering superior long-term results. When you factor in reduced water use, eliminated disease treatments, and improved harvest quality, organic fertilizers often cost less overall.
Transitioning Your Garden to Organic Fertilization

If you've previously used synthetic fertilizers, transitioning to organic methods takes patience but delivers lasting rewards:
Year One: Focus on rebuilding soil biology by adding compost and beginning regular liquid organic fertilizer applications. Expect results comparable to synthetic fertilizers as beneficial microbes colonize your soil.
Year Two: Soil structure improves noticeably. Plants show increased disease resistance and drought tolerance. You'll need less water and fewer pest interventions.
Year Three and Beyond: Your soil becomes a thriving ecosystem requiring minimal intervention. Plants grow vigorously with standard organic feeding schedules, and you'll notice improved flavor in vegetables and more prolific flowering in ornamentals.
Signs Your Plants Need Organic Fertilizer
Learning to read plant signals helps you provide appropriate nutrition:
Yellowing Leaves (Chlorosis): Often indicates nitrogen deficiency, especially if older leaves yellow first. Apply nitrogen-rich organic fertilizer promptly.
Slow Growth: Plants that seem stuck in neutral may lack balanced nutrition. Comprehensive liquid organic fertilizers address multiple potential deficiencies simultaneously.
Poor Flowering or Fruiting: Adequate nitrogen but insufficient phosphorus or potassium. Look for organic fertilizers with higher middle or last numbers in their NPK ratio.
Purple or Reddish Leaf Tints: May indicate phosphorus deficiency, particularly in cool weather when microbial activity slows.
Leaf Tip Burn or Brown Edges: Could signal potassium deficiency or inconsistent watering affecting nutrient uptake.
Making Organic Fertilizer Work for Your Garden
Success with organic fertilizers requires understanding that you're feeding soil life, not just plants directly. This fundamental shift in perspective transforms your relationship with your garden:
Instead of thinking "What does this plant need right now?" consider "How can I support the soil ecosystem that will feed this plant consistently?" This approach builds gardens that become healthier, more productive, and easier to maintain each year.
Ready to Transform Your Garden?
Understanding organic fertilizers empowers you to make informed decisions that benefit your plants, your family, and the environment. Whether you're growing a small container garden on your balcony or managing acres of vegetables, the principles remain the same: build soil life, feed consistently, and trust the natural processes that have sustained plant growth for millions of years.
Modern organic fertilizers like worm casting-based liquid formulas with hundreds of beneficial microbe species make this easier than ever before. They deliver fast results gardeners expect while building the long-term soil health that sustainable gardening requires.
Start Growing Better Today
Join 100,000+ gardeners who trust Elm Dirt's organic fertilizers for professional results without harmful chemicals. Every product is CDFA organic certified and backed by 5,000+ verified 5-star reviews.
Free Shipping on Orders Over $30
Shop All FertilizersYour garden deserves nutrition that works with nature, not against it. Every application of quality organic fertilizer represents an investment in healthier plants, safer food, and a cleaner environment. Start feeding your garden right today and discover why more than 100,000 gardeners have made the switch to proven organic nutrition that actually works.
Related Resources
Continue Learning About Organic Gardening
Need Help Choosing the Right Fertilizer?
Our plant care experts are here to help you select the perfect organic fertilizer for your specific needs.
14210 Norby Road, Grandview, MO 64030
About Elm Dirt
Elm Dirt provides premium organic plant nutrition trusted by master gardeners and professional landscapers across the United States. Our worm casting-based fertilizers combine traditional organic principles with modern microbiology to deliver fast-acting results while building long-term soil health. Every product is CDFA organic certified, third-party lab tested, and backed by thousands of verified customer reviews.